This potentially sight-threatening complication affects millions of Americans living with diabetes or prediabetes—estimated at over 100 million adults. Diabetic retinopathy develops when prolonged high blood sugar damages the delicate blood vessels supplying the retina, the light-sensitive tissue at the back of the eye responsible for capturing images and transmitting them to the brain via the optic nerve.
Left untreated, diabetic retinopathy can progress to severe vision loss or even permanent blindness. Early detection through specialized retinal imaging and timely intervention are critical to preserving your sight.
What Is Diabetic Retinopathy?
The retina requires a rich, continuous blood supply delivered through a network of tiny vessels. In diabetes, chronically elevated blood glucose weakens these vessels, leading to leakage of fluid, blood, and lipids into the retinal tissue. This can cause swelling (macular edema), hemorrhages, microaneurysms, and, in advanced stages, abnormal new vessel growth (neovascularization), scarring, and tractional retinal detachment.
Diabetic retinopathy often progresses silently in its early stages (non-proliferative diabetic retinopathy, or NPDR), with no noticeable symptoms. As it advances to proliferative diabetic retinopathy (PDR) or diabetic macular edema (DME), patients may experience blurred vision, floaters, dark spots, or sudden vision changes.
Are You at Risk?
Anyone with type 1 or type 2 diabetes is at risk, but certain factors increase the likelihood and severity:
Poorly controlled blood sugar (elevated HbA1c)
Longer duration of diabetes
Co-existing hypertension or high cholesterol
Pregnancy (including gestational diabetes)
As retina specialists, we emphasize that strict glycemic control, blood pressure management, and lipid control can significantly slow or prevent progression.
What to Expect During a Diabetic Retinopathy Evaluation
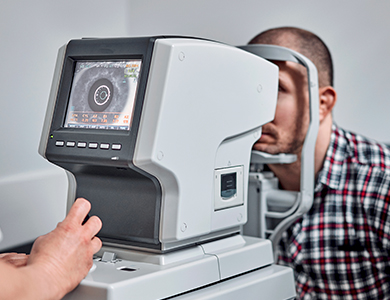
At this practice, we perform comprehensive dilated retinal examinations tailored for diabetic patients. This includes:
Pupil-dilating drops (which may temporarily blur vision and cause mild stinging)
High-resolution fundus photography and optical coherence tomography (OCT) to capture detailed images of the retina and assess for swelling or fluid
Fluorescein angiography (when needed) to evaluate blood vessel integrity
The exam is non-invasive, painless, and quick. We also assess visual acuity and discuss your diabetes management.
Early detection allows us to monitor subtle changes and intervene promptly—often before symptoms appear. If diabetic retinopathy is present, we develop a personalized treatment plan, which may include intravitreal injections (anti-VEGF therapy), laser photocoagulation, or, in advanced cases, vitreoretinal surgery.
If you have diabetes, schedule regular evaluations with a retina specialist. Early intervention can make all the difference in preserving your vision. Contact our team today for more information or to arrange your comprehensive retinal assessment.